样例说明
通过本样例,您可以了解:
- 业务插件包的动态加载样例
- 自定义ClassLoader的扩展机制
环境准备
您需要:
- 用于运行程序的IDE(集成开发环境),比如IntelliJ IDEA 或其类似工具;
- Java™ Development Kit (JDK),需要JDK 8及以上版本
- 已经完成Nacos安装,并能正常运行
- 已经完成 Quickstart Guide 样例
版本依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hiforce.lattice</groupId>
<artifactId>lattice-model</artifactId>
<version>1.0.13</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hiforce.lattice</groupId>
<artifactId>lattice-runtime</artifactId>
<version>1.0.13</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hiforce.lattice</groupId>
<artifactId>lattice-dynamic-loading</artifactId>
<version>1.0.12</version>
</dependency>动态加载业务包演示
业务包的动态加载机制,可以针对某些场景下,可以将云市场里的应用插件,下载并安装到当前的容器中。云市场样例:
本例主要演示,如何基于Lattice构建的业务包,实现动态加载,并不包含云市场本身的构建。
在 lattice-sample 中,可以参考 lattice-dynamic-load-apps 这个demo,配置Lattice插件加载目录是定义,在application.properties 中的,如下:
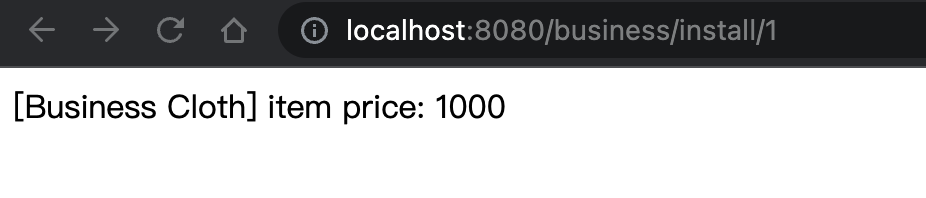
lattice.plugin.dirs=/Users/rocky/code/plugins然后我们启动 org.hiforce.lattice.dynamic.LatticeDynamicStarter 这个Starter。在浏览器中,打开 http://localhost:8080/business/install/1 ,可以看到如下输入:
接着,我们继续输入 http://localhost:8080/business/install/2 ,可以看到如下结果:
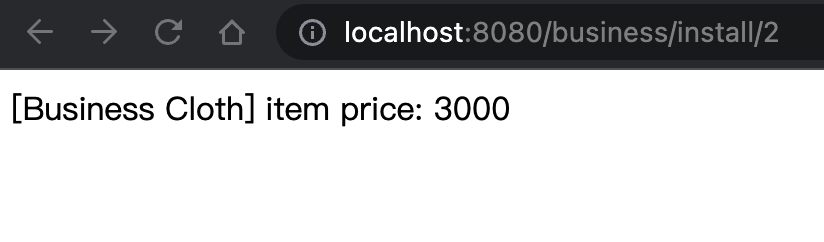
可以看到,业务包动态加载替换成新版本了。
刚刚输入的网址对应的Controller代码如下:
@RequestMapping("/business/install/1")
public String installBusinessPlugin_1() {
clear();
String urlStr = "/apps/lattice-business-cloth-1.0.0-SNAPSHOT.jar";
URL url = DynamicLoadTestController.class.getResource(urlStr);
if (null != url) {
File file = new File(url.getPath());
LatticeDynamic.getInstance().installPlugin(new PluginFileInfo(file));
}
return invokeBusinessPlugin();
}
@RequestMapping("/business/install/2")
public String installBusinessPlugin_2() {
clear();
String urlStr = "/apps/lattice-business-cloth-1.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar";
URL url = DynamicLoadTestController.class.getResource(urlStr);
if (null != url) {
File file = new File(url.getPath());
LatticeDynamic.getInstance().installPlugin(new PluginFileInfo(file));
}
return invokeBusinessPlugin();
}Spring & Spring MVC 的动态安装
在上面例子基础上,我们对Cloth业务插件包增加Spring Bean以及SpringMVC的定义,如下:
@Service
public class ClothService {
public String helloCloth() {
return "Hello Cloth";
}
}
@RestController
public class ClotController {
@Autowired
private ClothService clothService;
@RequestMapping("/cloth")
public String cloth() {
return clothService.helloCloth();
}
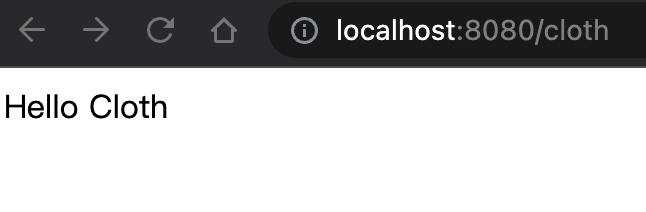
}我们在浏览器中输入 http://localhost:8080/business/install/3, 完成 业务插件包 1.0.3 版本安装。然后,再输入 http://localhost:8080/cloth , 我们可以看到这个SpringMVC动态注册成功了。 成功后的界面如下:
Lattice自定义ClassLoader
在 Lattice 框架中,提供了自定义ClassLoader的SPI,定义如下:
public interface CustomClassLoaderSpi {
ClassLoader getCustomClassLoader();
}在本例中,我在Lattice里框架中提供了一个非常简陋的基于URLClassLoader的加载方案,在 lattice-dynamic-loading 中,定义了LatticeDynamicClassLoaderBuilder,他能够实现对指定目录下的插件包进行加载,如下:
@AutoService(CustomClassLoaderSpi.class)
public class LatticeDynamicClassLoaderBuilder implements CustomClassLoaderSpi {
@Override
public ClassLoader getCustomClassLoader() {
String[] dirs = LatticeDynamicProperties.getInstance().getPluginDirs();
List<URL> urls = Lists.newArrayList();
for (String dir : dirs) {
urls.addAll(buildJarURLList(dir));
}
URL[] urlArrays = urls.toArray(new URL[0]);
return new URLClassLoader(urlArrays, LatticeDynamicClassLoaderBuilder.class.getClassLoader());
}
private List<URL> buildJarURLList(String dirStr) {
List<URL> urls = Lists.newArrayList();
try {
File dir = new File(dirStr);
if (!dir.exists() || !dir.isDirectory()) {
return Lists.newArrayList();
}
File[] jars = dir.listFiles(pathname -> pathname.getPath().endsWith(".jar"));
if (null == jars) {
return urls;
}
for (File file : jars) {
urls.add(new URL("file:" + file.getPath()));
}
return urls;
} catch (Exception ex) {
return Lists.newArrayList();
}
}
}Lattice框架用户,可以基于这个机制,编写出更加复杂的插件加载方案。比如,
- 可以进一步增强,对不同业务身份进行加载机制隔离
- 可以让业务插件打包成 flat-jar,每个业务甚至可以自行引入其他第三方包
这些,将不会在官方Lattice框架中提供。
发表回复